#include "../config.h"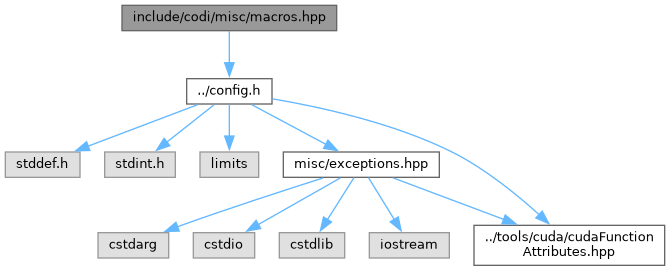
Go to the source code of this file.
Classes | |
| struct | codi::CODI_UNION< First > |
| Creates a union of interface definitions. More... | |
Namespaces | |
| namespace | codi |
| CoDiPack - Code Differentiation Package. | |
Macros | |
| #define | CODI_ENABLE_CHECK(option, condition) (!(option) || (condition)) |
| #define | CODI_IS_CPP14 (201402L <= __cplusplus) |
| Check for CPP 14 standard. | |
| #define | CODI_IS_CPP17 (201703L <= __cplusplus) |
| Check for CPP 17 standard. | |
| #define | CODI_TO_STRING(expression) CODI_TO_STRING2(expression) |
| Conversion macro. | |
| #define | CODI_TO_STRING2(expression) #expression |
| Conversion macro. | |
| #define | CODI_UNUSED_ARG(arg) /* arg */ |
| Used in a constexpr context, where using CODI_UNUSED spoils the constexpr. | |
| #define | CODI_WRAP_FUNCTION(NAME, FUNC) |
| Wrap a function in a function object. Used for performance optimizations. | |
| #define | CODI_WRAP_FUNCTION_TEMPLATE(NAME, FUNC) |
| Wrap a function in a function object. Used for performance optimizations. | |
Default template type declarations | |
These templates are used to employ the design guideline for the default definitions of template arguments. See Template declarations for Details. | |
| #define | CODI_ANY int |
| Used in default declarations of expression templates. | |
| #define | CODI_DD(Type, Default) Type |
| Abbreviation for CODI_DECLARE_DEFAULT. | |
| #define | CODI_DECLARE_DEFAULT(Type, Default) Type |
| #define | CODI_IMPLEMENTATION ImplProxy |
| Used in interface declarations to indicate the type of the implementing class. | |
| #define | CODI_STATIC_ASSERT(cond, message) static_assert(cond, message) |
| Static assert in CoDiPack. | |
| #define | CODI_T(...) CODI_TEMPLATE(__VA_ARGS__) |
| Abbreviation for CODI_TEMPLATE. | |
| #define | CODI_TEMPLATE(...) __VA_ARGS__ |
| Expand template types in preprocessor macros. | |
| #define | CODI_UNDEFINED void |
| Used in interface declarations for types that have to be defined in the specializations. | |
| #define | CODI_UNDEFINED_VALUE false |
| Used in interface declarations for variables that have to be defined in the specializations. | |
Functions | |
| template<typename... Args> | |
| void | codi::CODI_UNUSED (Args const &...) |
| Disable unused warnings for an arbitrary number of arguments. | |
| #define CODI_DECLARE_DEFAULT | ( | Type, | |
| Default | |||
| ) | Type |
CODI_IDE can be defined to use the default declaration of type names. This enables auto completion in the IDEs.
Every using declaration in all CoDiPack classes should declare its variables as: using TYPE = CODI_DECLARE_DEFAULT(T_TYPE, Default);
| #define CODI_ENABLE_CHECK | ( | option, | |
| condition | |||
| ) | (!(option) || (condition)) |
Check the condition only if the option is true, otherwise the result is always true. Used like if(CODI_ENABLE_CHECK(option, condition)) {...}, option == false means that the if body is always executed.
| #define CODI_WRAP_FUNCTION | ( | NAME, | |
| FUNC | |||
| ) |
Wrap a function in a function object. Used for performance optimizations.
| #define CODI_WRAP_FUNCTION_TEMPLATE | ( | NAME, | |
| FUNC | |||
| ) |
Wrap a function in a function object. Used for performance optimizations.